

10 Steps to Ensure Workplace Safety Using Proper Strapping Techniques
In the world of packaging and logistics, strapping operations play a critical role in securing loads for transportation and storage. Whether it’s bundling products together or securing them to pallets, the importance of strapping cannot be overstated. However, with the benefits of strapping come inherent risks if not performed correctly. Ensuring workplace safety through proper strapping techniques is essential for protecting workers, maintaining product integrity, and preventing accidents.

The Importance of Safety in Strapping Operations
Worker Protection
Strapping operations involve the use of high-tension tools and materials, which can pose significant hazards if not handled properly. Injuries can range from minor cuts and bruises to severe lacerations, musculoskeletal disorders, and even fatalities. Prioritizing safety in strapping operations helps protect workers from these potential hazards.
Product Integrity
Improper strapping can lead to load instability, resulting in damaged goods during transit. Securely strapped products ensure that they arrive at their destination in optimal condition, reducing the risk of financial losses and customer dissatisfaction.
Accident Prevention
Accidents related to strapping operations can cause disruptions in the workflow, leading to delays and increased costs. Implementing safe strapping practices helps prevent accidents, ensuring a smooth and efficient operation.
Guidelines for Safe Strapping Practices
1. Training and Education
Proper training is the foundation of safe strapping operations. Employees should receive comprehensive training on the correct use of strapping tools and equipment, including:
- Tool Operation: Understanding how to operate both manual and powered strapping tools correctly.
- Material Handling: Knowing how to handle strapping materials to avoid injuries.
- Safety Protocols: Familiarity with safety protocols and emergency procedures in case of an accident.
2. Use Appropriate Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Wearing the right PPE is crucial for protecting workers during strapping operations. Essential PPE includes:
- Gloves: To protect hands from cuts and abrasions.
- Safety Glasses: To shield eyes from flying debris and tensioned strap ends.
- Steel-Toed Boots: To safeguard feet from heavy objects that might fall during strapping.
3. Select the Right Strapping Material
Choosing the appropriate strapping material is vital for both safety and effectiveness. Common strapping materials include:
- Polypropylene (PP) Strapping: Suitable for light to medium loads.
- Polyester (PET) Strapping: Ideal for heavy loads and has high tensile strength.
- Steel Strapping: Used for securing very heavy loads but requires careful handling due to its sharp edges.
Each material has specific applications and safety considerations. For instance, steel strapping requires additional precautions to prevent cuts from sharp edges.
4. Inspect Tools and Equipment Regularly
Regular inspection and maintenance of strapping tools and equipment are critical for ensuring their safe operation. Check for:
- Wear and Tear: Inspect tools for any signs of wear and tear that might compromise their functionality.
- Proper Functioning: Ensure that all moving parts are working correctly and smoothly.
- Battery Life: For battery-powered tools, check battery life and replace or recharge as necessary.
5. Follow Correct Tensioning Techniques
Proper tensioning of straps is essential for secure and safe load securing. Over-tensioning can damage the product and increase the risk of strap breakage, while under-tensioning can lead to load instability. Guidelines for correct tensioning include:
- Manufacturer’s Recommendations: Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for the specific strapping tool and material.
- Consistent Tension: Apply consistent tension to avoid uneven securing.
- Adjustable Settings: Use adjustable tension settings if available on the strapping tool to match the load requirements.
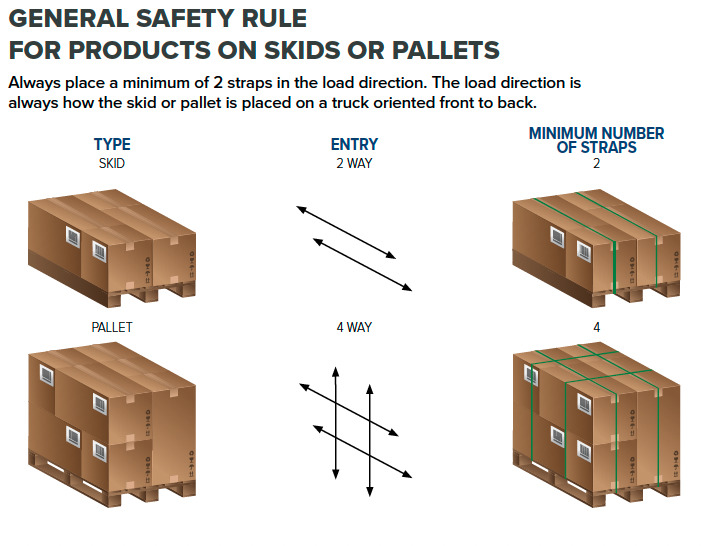
6. Secure Strap Ends Properly
Securing the ends of the straps correctly is crucial to ensure the load remains stable. Depending on the strapping material, different methods can be used:
- Seals and Buckles: For heavy-duty plastic strapping, use seals and buckles to secure the strap ends.
- Heat Sealing: For plastic strapping, use heat sealing tools to fuse the ends together securely.
- Friction Welding: Some strapping tools use friction welding to bond the strap ends without additional seals.
7. Maintain a Clean and Organized Workspace
A cluttered and disorganized workspace can lead to accidents and injuries. Maintain a clean and organized area for strapping operations by:
- Clearing Debris: Remove any debris or obstructions that could cause tripping or interfere with strapping tools.
- Organizing Tools: Keep strapping tools and materials neatly organized and within easy reach.
- Proper Lighting: Ensure adequate lighting in the workspace to improve visibility and reduce the risk of accidents.
8. Implement Ergonomic Practices
Strapping operations can be physically demanding, leading to musculoskeletal injuries if not performed ergonomically. To reduce the risk of such injuries:
- Adjust Workstations: Set up workstations at appropriate heights to minimize bending and reaching.
- Use Lifting Aids: Utilize lifting aids or assistance for heavy loads to reduce strain on the body.
- Encourage Breaks: Promote regular breaks and stretching exercises to prevent fatigue and muscle strain.
9. Monitor and Review Safety Practices
Regular monitoring and review of safety practices ensure continuous improvement and adherence to safety protocols. Conduct:
- Safety Audits: Perform regular safety audits to identify potential hazards and areas for improvement.
- Feedback Sessions: Encourage feedback from employees on safety practices and any concerns they may have.
- Incident Reports: Analyze incident reports to understand the causes of accidents and implement preventive measures.
10. Foster a Culture of Safety
Creating a culture of safety within the workplace is essential for the sustained success of safe strapping operations. This involves:
- Leadership Commitment: Management should demonstrate a commitment to safety by prioritizing it in all operations.
- Employee Involvement: Involve employees in safety discussions and decision-making processes.
- Continuous Improvement: Encourage continuous improvement in safety practices through regular training and updates.
Conclusion
Ensuring workplace safety with proper strapping techniques is not just about compliance with regulations; it’s about protecting workers, maintaining product integrity, and preventing costly accidents. By following these guidelines and fostering a culture of safety, companies can achieve safer and more efficient strapping operations, ultimately contributing to the overall success and well-being of the organization. Remember, safety first is not just a motto—it’s a commitment to excellence in every strapping operation.
